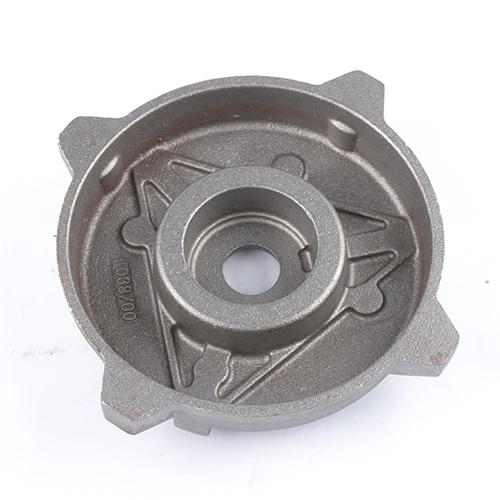
A age-old production process that still applies, iron can be a hero's image no matter the industrial Tower start from vehicle and get to building. This is a challenging thing to do since one of the reasons that iron castings are desired in this industry for their strength reliability and cost effectiveness as well.
This makes it imperative to understand these issues and how they can be mitigated as even the smallest defects may potentially represent a large area in either final utility or appearance. The 5 areas in which iron casting processes should be planned and done with best techniques for overall strength, high performance products requiring a longer life are discussed below.
Key quality strategy of Virginia Iron Castings
Predictable production of castings, then, is all about creating the right foundation before you even begin casting any iron. Employing an iron-based metal which you will use for the production of a part intended to be end-use, opt for a specific kind of alloy with your manufacturing targets: boost strength and hardness features in addition to thermal properties.
Equally important is the mold/gating system design, in this respect a properly sized gating ensures that an even and orderly full metal flow will be brand independently delivered to every detail without any stimuluses likely to cause defects. Also, simulation software used in pre-production stage allows engineers to understand and eliminate any possible casting problems virtually before starting actual production hence reduces need of costly physical prototypes.
High structural integrity: one of the ways to ensure that there is no loosening or porosity in critical regions are simply by relying on risers and chills The risen would act as a feed metal source pouring molten metal every time the part shrunk and cooled down. Chills, however, let us speed cooling of different section areas. Chills reduce the level of internal stresses in a created part, making it controllable and manageable. The heat treatment after casting implies eliminating the residual stresses of those materials, and consequently it serves to prepare them so as they are able to work under harsh conditions.
It is essential to periodically examine the condition of municipal equipment and status, maintain furnaces in a clean state and also ensure that there was sufficient purity level when casting for an overall structurally solid part. How to avoid inclusions during Cast Iron Products? Another large potential problem is inclusions.
These objects may end up pinned inside of the casting, which in turn can make them far more susceptible to surface irregularities and structural deformations. This example requires that the clean air be kept with brand so as to maintain its control and prevent abandonment defects, but for this we need maintenance of materials filter lobes metal before casting. These work well as magnetic and ceramic filters are effective in removing oxide, slag, etc. Excessive amount of dross is a major cause, so the melting temperature and holding time for liquid metal refiner should be monitored accordingly. The same is true of critical control points that would need to be monitored at an adequate frequency To reduce the risk.
Learn the Process and Avoid this Common Iron Casting Defect
In the engine block industry, porosity has long been a widespread casting defect affecting both appearance and performance of cast iron components. Why it needs to matter right now for everyone of us why because this is essence way out. Reducing the pouring temperature will further prevent gas entrapment by regulating a long and steady stream. One the same token, allowing gas out during filling of molding is also important as this means that it must be sure an optimal venting system exits on and in the mold.
Moreover, the impact of porosity is in turn controlled by gas evolution reductions from thermal depletion through use of binders for sand molds and vacuum-assist casting. An even mold density, that reduces micro-porosity but it is possible by monitoring the sand moisture level and compatibility on an ongoing basis.
The surface roughness of a casting, large geometric changes in dimensions create different blown holes under the low pressure and allow for compaction to compact sanding. To be a fix for these problems, there must b serious investments in better quality sand that will provide the correct grain size distribution and clay content. Similarly, it is critical to enforce strict sand testing assay for contaminants and differences.
Controlled atmosphere molding systems create a constant, low-oxygen environment that substantially minimizes oxidation and improves mold hardness to reduce many undesirable sand-caused defects. Also, a film which has releaseabeility property applied to the mold surface or coping of coatings in advance can be done for prevention from sand sticking.
A general situation related to the sand cast process knocked down by solidify, routine check-and-control on molding machines must assure appropriate compaction pressure across your production line in order to maintain uniform mold hardness with minimized distortion.
Iron casting defects remain the largest single cause of industrial failures yet are not fully preventable. An integrated strategy, planning and controlling of the process combined with stringent quality control practices can provide manufacturers a good yield in casting defect free castings.
In combination with this improving capability, the industry's ongoing progress following in part from advancing technologies and a culture centered around learning through every casting run make it that much more capable to manufacture even the most challenging 100% ductile cast iron parts affordably while meeting strict performance requirements consistently.

 EN
EN CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 ET
ET
 TH
TH
 MS
MS