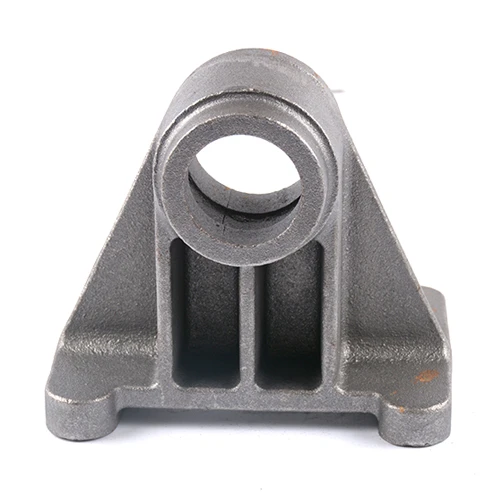
Metal fabrication is an amazing trade where buildings are being serviced with lots of industrial parts mas made as helpful components for automotive industries, Agriculture and Construction Machinery. In this blog we discussed how iron casting is made and why it matters, the benefits of iron casting.
Types of Metal Casting
The techniques in Metal casting used a wide variety of these depending on the characteristics and requirements with certain metals being cast. Other foundry technologies to note are plaster mold, high pressure die castings and sand and permanent mould. While sand casting meets the versatile processes of complex geometries, die-casting allows manufacturers to produce intricate components with a volume production. Precision Casting Iron way most costlyMost design work is done by investment careful and it gets more expensive than the others.
Conversely, permanent mold casting delivers consistent and precise outcomes typically used in aluminum alloys as well as magnesium.
Advantages of Iron Casting
It is hard, strong and amenable to casting into numerous forms. Because the iron body can resist greater intensity of stress (so this cast material is appropriate for casting in a few high mechanical properties designs). That is, vibration from components like engine blocks and machine mounts are absorbed by the Grey Cast Iron.
Other Methods of Iron Casting
Boasts fantastic wear characteristics and is quite a bit lighter compared to many other competing aluminum castings which can easily become an iron equivalent casting. In examples such as automotive parts, aluminum is lighter than iron for the same application but has almost three times lower density and a relatively similar strength to tensile with its thermal conductivity being probably far more suitable.
While steel was strong enough to produce more complex shapes, iron remained cheaper than and not so expensive that it would have been typically better. While investment casting is certainly precise, the cost-effective volume production of large parts cannot touch iron sand casting.
Differences in Iron Casting The argument indicated that iron casting comprises how iron can be applied in extremely thick-walled molds an advantage lightweight metals don’t have in direct contrast to hot grip designs and iron. Most importantly, iron is fundamentally different from Light metal casts in that an individual looks at the graphite unturned alloy.
The unreturned graphite There are two obvious factors because it angles iron in how it is machined and damping. In terms of being machined, it can be said that the graphite unreturned has made it possible for iron or for companies to gear that the supply of ductile iron containing graphite nodules remains available worldwide. Green Concerns Sustainable manufacturing is a term used to refer to the process as many manufactured items will be less harsh to the environment by minimizing wastage and making the production processes less environmentally harmful. of iron castings in our foundry requires us to consume a lot of energy.
We are accepting as much environmental countermeasure as possible. We engage in a considerable amount recycling items like scrap iron, which is important because it essentially reduces their manufacture, saving natural resources. Iron castings also have a low as well carbon footprint than aluminum, which also consumes high smelting processing energy and also recycling energy. The best way out is through both the industries and to electroscope by having the best process control and using renewable sources as well as clean energy.
Steel casting is considered applicable for severe service, where high strength and wear resistance are required. The durability of investment casting is, in addition, how it still outperforms other metal casting procedures to this day. This focus on technology and sustainability will secure the future of iron casting in a creative dependent manufacturing environment.

 EN
EN
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 ET
ET
 TH
TH
 MS
MS